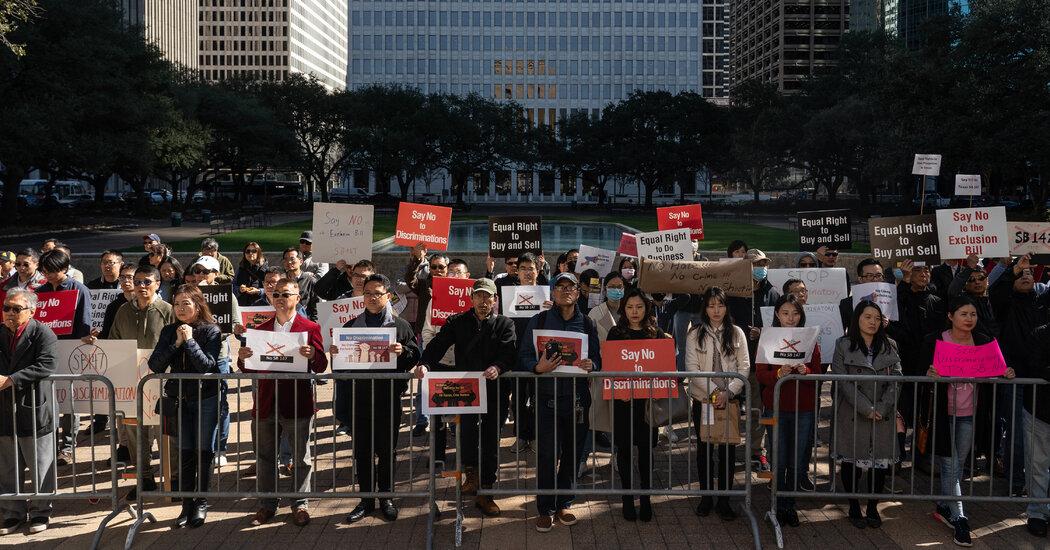
The share of United States farmland owned by Chinese people and companies is small and has not been growing substantially. Chinese owners held about 350,000 acres at the end of 2020, according to a U.S. Department of Agriculture report, and most of the farmland came from the Chinese acquisition of Smithfield Foods in 2013. Canadian owners, by contrast, held 12.4 million acres.
The figures do not include residential or commercial buildings, though that has largely not been the focus of most legislative efforts. Chinese investors are among the top foreign purchasers of residential real estate, along with Canadians, according to the National Association of Realtors.
Other states have had concerns over foreign ownership of land and have made efforts to regulate it. Some states, including Minnesota and Iowa, have enacted bans on foreign ownership of agricultural land, and a larger number place restrictions on such purchases. The Oklahoma Constitution limits land ownership to U.S. citizens. Those laws, unlike the proposal in Texas, do not single out citizens of particular countries.
In Canada, a sweeping ban on foreign ownership of residential property went into effect this year — a move that the country’s liberal leadership said was aimed at curbing soaring housing prices.
However, the proposed ban in Texas, endorsed by Mr. Abbott, appears to go further than the laws adopted in other U.S. states, both in applying to all “real property” — including urban buildings or condominium apartments — and in applying its provisions not only to the governments of certain countries but also to their citizens.
During its last session, in 2021, the Texas Legislature barred companies from the same list of countries targeted in the new proposed law from winning contracts that relate to “critical infrastructure” in the state, including the electricity grid, water treatment plants, and cybersecurity and communications systems.
That bill came in response to the plan by the Chinese billionaire, Sun Guangxin, to construct a wind farm that would have connected to the Texas electricity grid. The bill passed with bipartisan support in the State Senate, and Mr. Abbott signed it.