Jing Qian is vice-president of the Asia Society and managing director of its Centre for China Analysis (CCA), which he co-founded with Kevin Rudd, former prime minister of Australia. His research examines the interplay between domestic politics and foreign policy in the United States and China.
Advertisement
This outcome was largely anticipated. The Stockholm joint communique explicitly referenced the Geneva joint statement – the leader-level blueprint endorsed by both presidents that set out core principles – and portrayed the London talks as a continuation. This framing makes it useful to review the progression from Geneva.
Advertisement
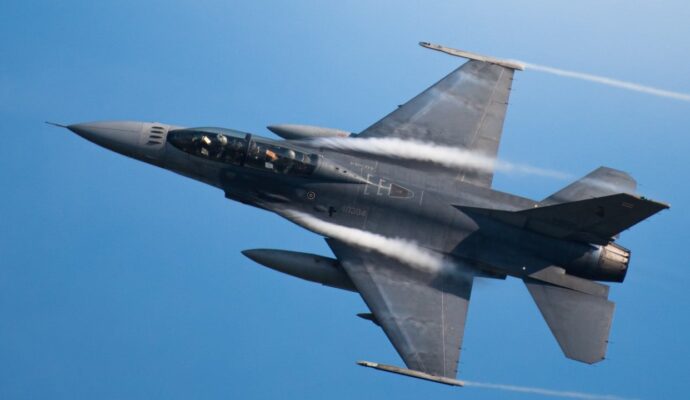
When US and Chinese negotiators gathered in mid-May in Geneva, de-escalation was their shared interest. Markets were rattled, global forecasts had been dimmed and both Beijing and Washington needed breathing space.
Around the table sat US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent and US Trade Representative Jamieson Greer. They faced China’s Vice-Premier He Lifeng, backed by veteran negotiators – Vice-Minister of Finance Liao Min and Vice-Minister of Commerce Li Chenggang – described by their US counterparts as “tough”.


